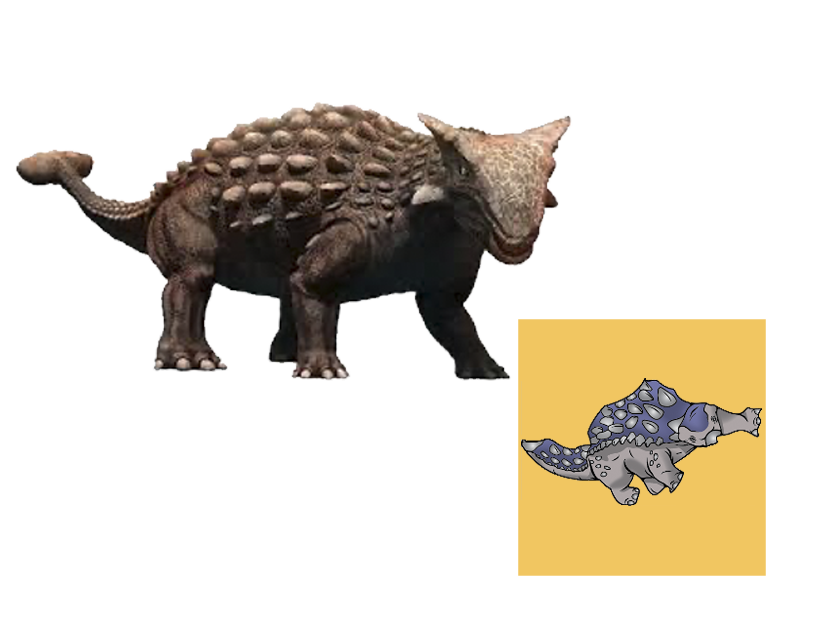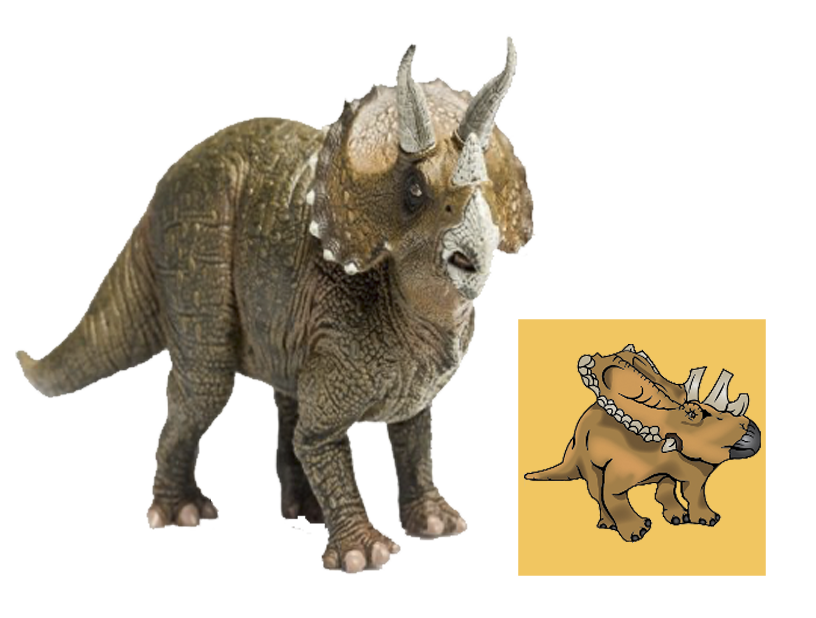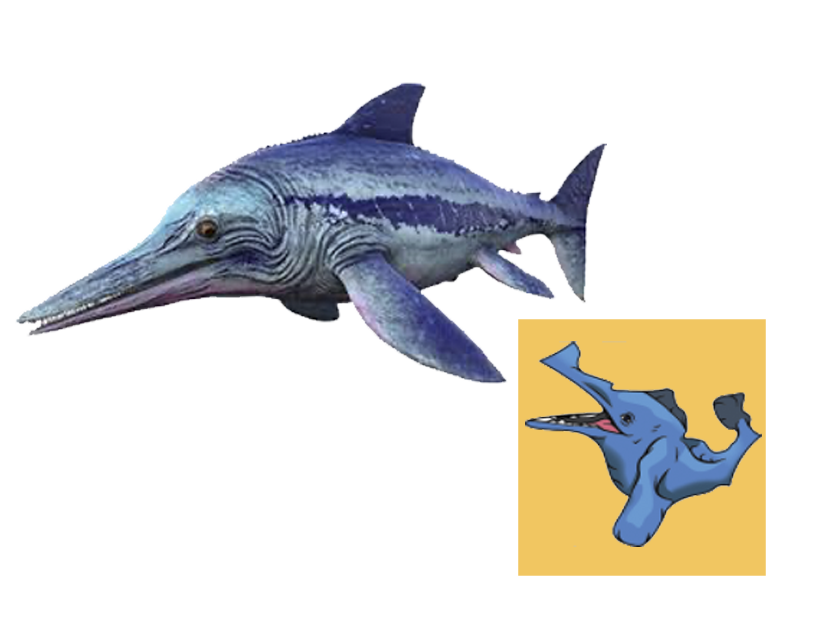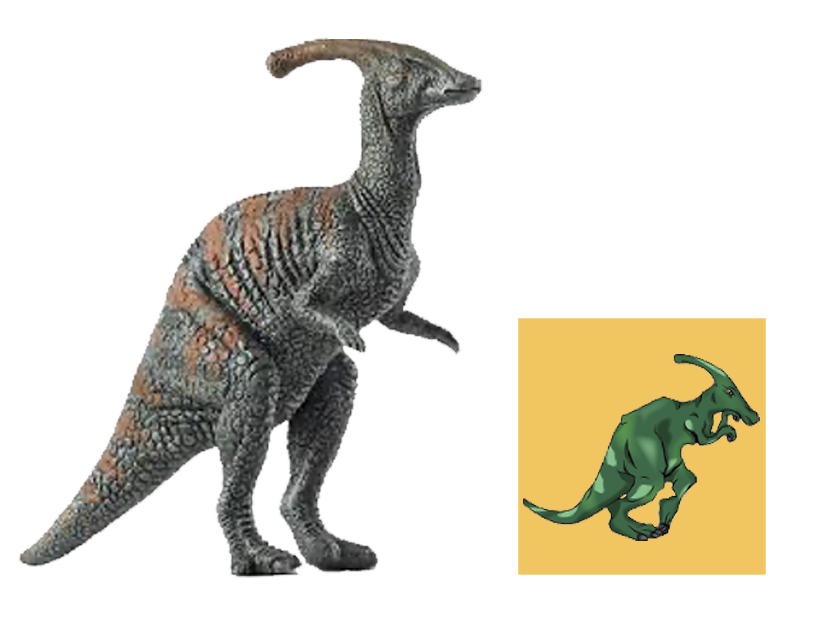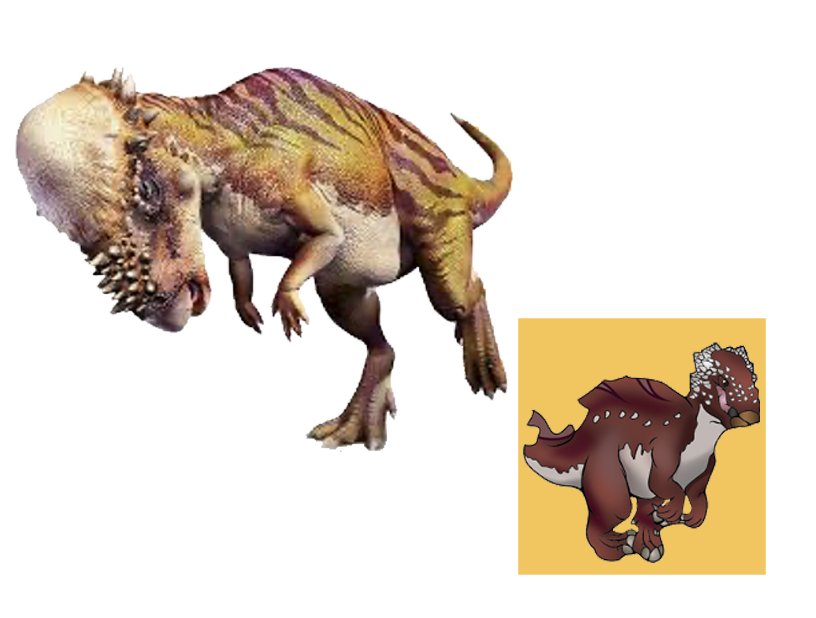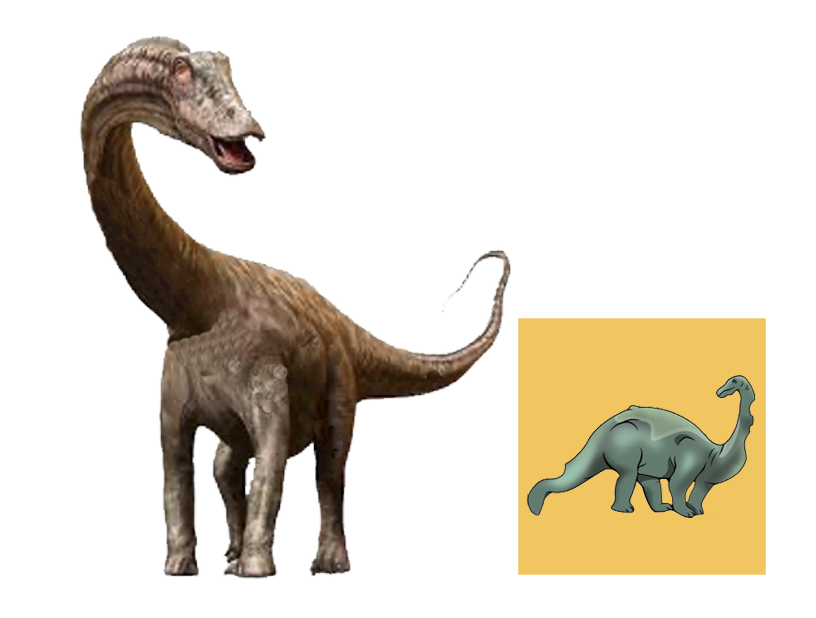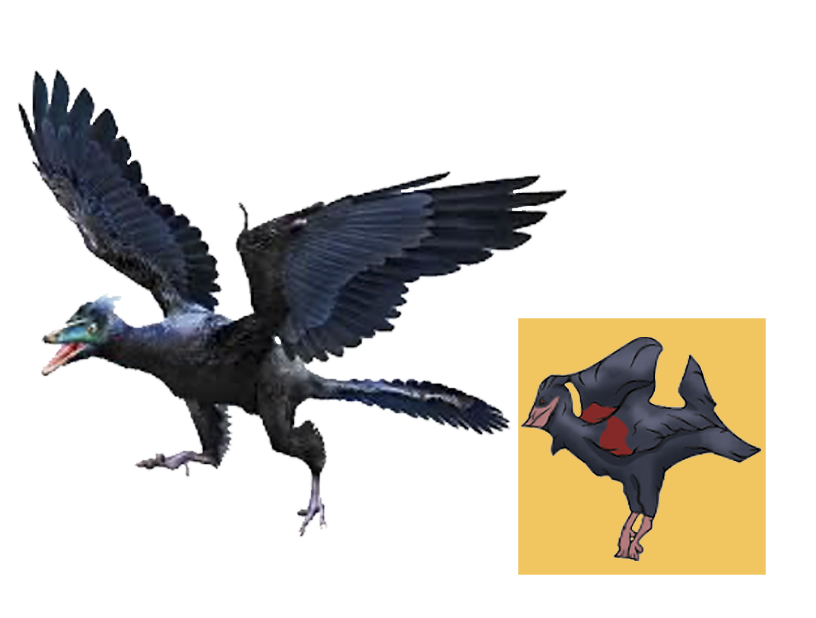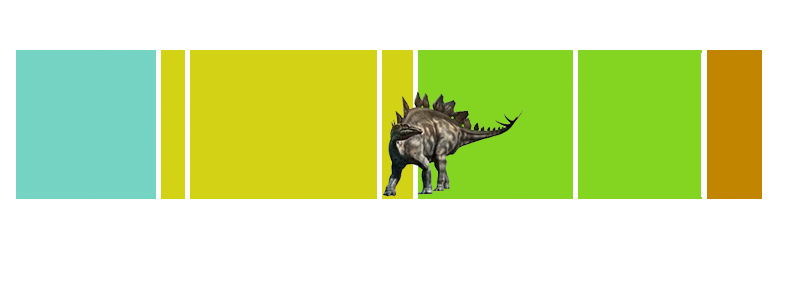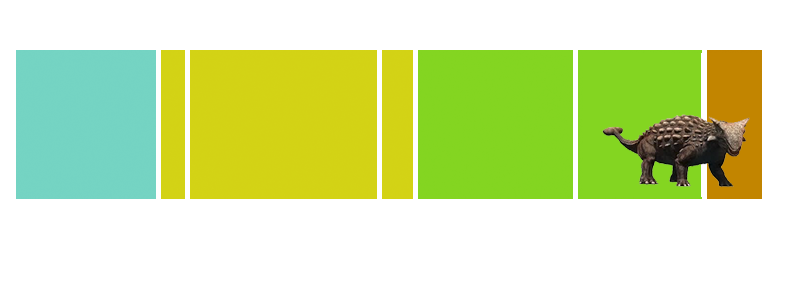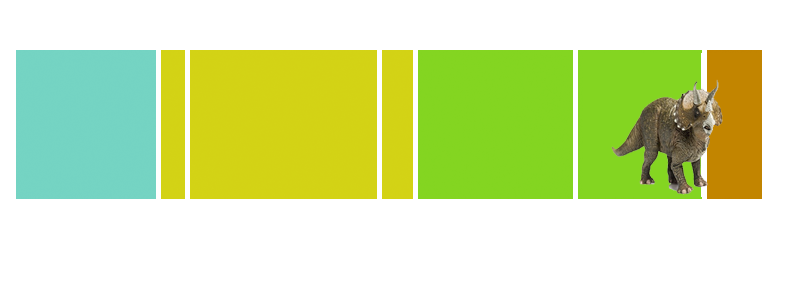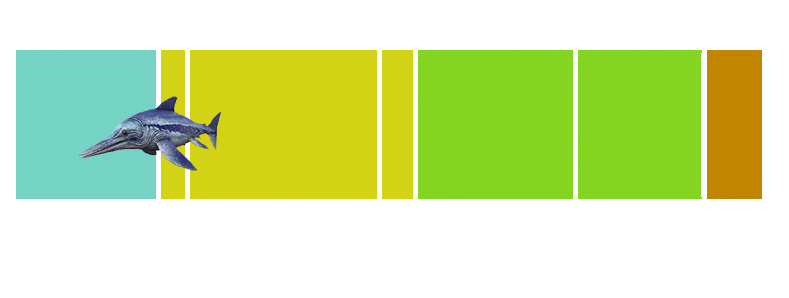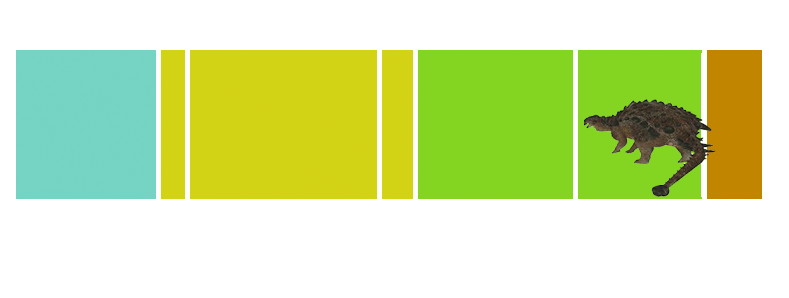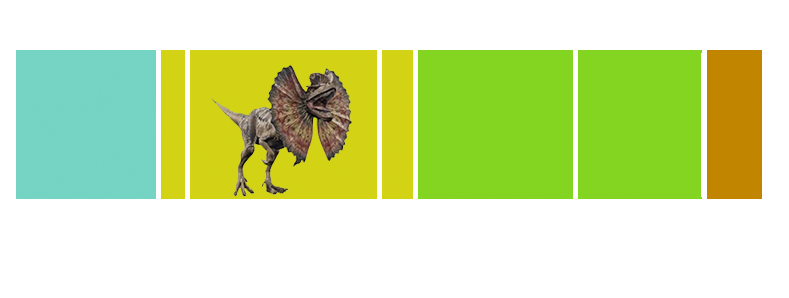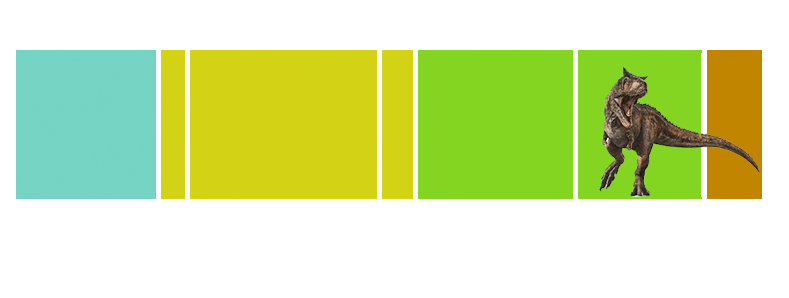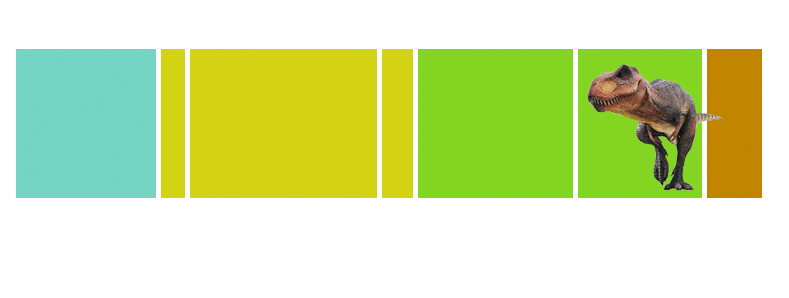














| Anbanguera: | 'old devil'. Long sharp toothed jaws. |
| Pteranodon: | 'toothless'. No teeth, but a long crest on its head. |
| Quetzalcoatlus: | It is named after a legendary feathered serpent god of Mexico. |
| Ornithocheiru: | 'bird hand'. Fossil found in England. |
| Rhamphorhynchus: | 'beak snout'. Had short legs and a long bony tail. |